Workload Estimation Using PERT Method
The estimation calculators are designed for planning labor costs in software projects.
For this purpose, the following tools are available:
- Software design workload estimation calculator (for analyst tasks);
- Software development workload estimation calculator (for programmer tasks).
The calculators use the PERT estimation methodology. This approach accounts for uncertainty in the workload of individual tasks.
According to Sergey Arkhipenkov, this is the most pragmatic approach that provides sufficiently realistic estimates of project workload and timeline quickly and with minimal overhead.
The PERT (Program/Project Evaluation and Review Technique) estimation method was developed in 1958 during the Polaris submarine-launched ballistic missile project.
The input for this estimation method is a list of elementary work packages. The engineering approach doesn't require knowing the exact distribution of our workload estimate for each such elementary package. The uncertainty range can be sufficiently characterized by three estimates:
- Mi — Most likely workload estimate.
- Oi — Minimum possible workload for the work package. No risks materialized. We definitely can't complete it faster. The probability of achieving this estimate is 0.
- Pi — Pessimistic workload estimate. All risks materialized.
The average workload estimate for each elementary package can be determined by the formula:
Ei = (Pi + 4Mi + Oi)/6.
For calculating standard deviation, the following formula is used:
SDi = (Pi - Oi)/6.
If our workload estimates for elementary work packages are statistically independent and not biased by, for example, unjustified optimism, then according to the Central Limit Theorem of probability theory, the total project workload can be calculated as:
Е = ∑ Ei
And the standard deviation for the total workload estimate would be:
Then for estimating the total project workload that we won't exceed with 95% probability, we can use the formula:
E95% = E + 2 * SD.
This means the probability of the project exceeding this workload estimate is only 5%. This is already quite an acceptable estimate that a professional manager can stand behind.
In our case, we've attempted to apply this approach to estimating the workload of individual software development or design tasks. The purpose of these calculators is to generate a justified workload estimate that can be included in a JIRA task description.
Based on several custom software development projects, we've compiled a nomenclature of predefined tasks used for workload estimation:
- nomenclature of standard tasks for software design analysts;
- nomenclature of standard tasks for software developers.
However, the existence of a predefined task list doesn't restrict you from modifying these task descriptions as needed for your specific project.
The button functions are illustrated in the figure below.
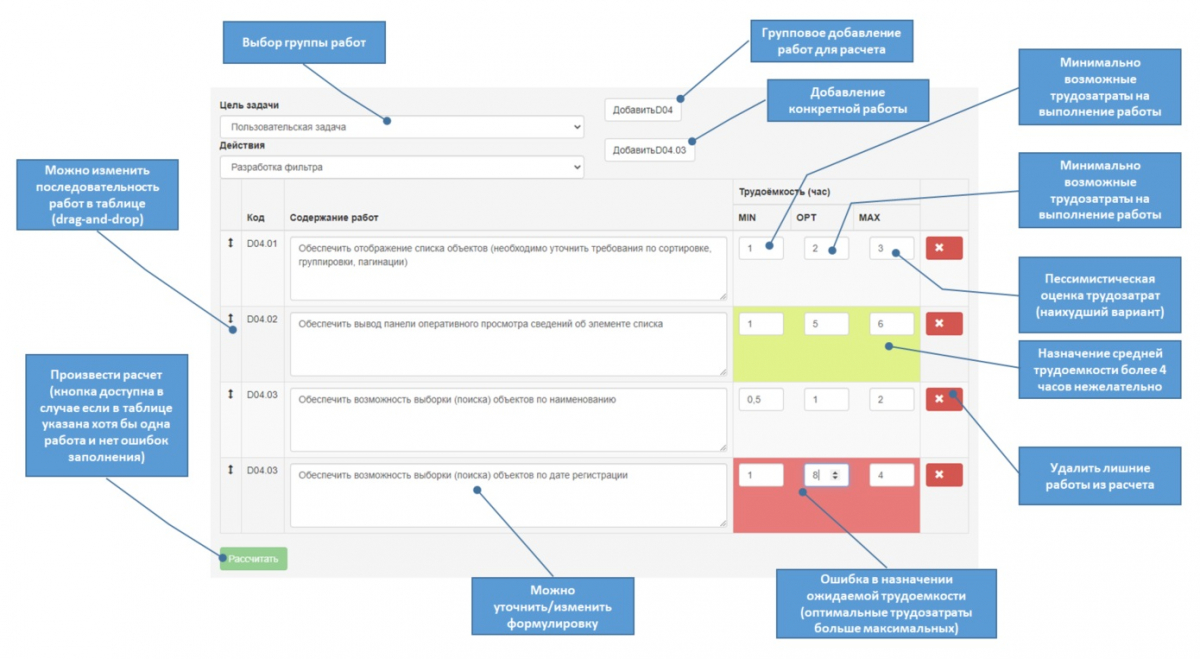
Fig. 1. Calculator button functions
After compiling the list of tasks required to complete the work item, clicking the "Calculate" button will provide the expected workload for solving the task, including the necessary time buffer.

Fig. 2. Example of calculation results
The resulting calculation can be copied to the clipboard and pasted into a JIRA task description.

Fig. 3. Copying results to JIRA
